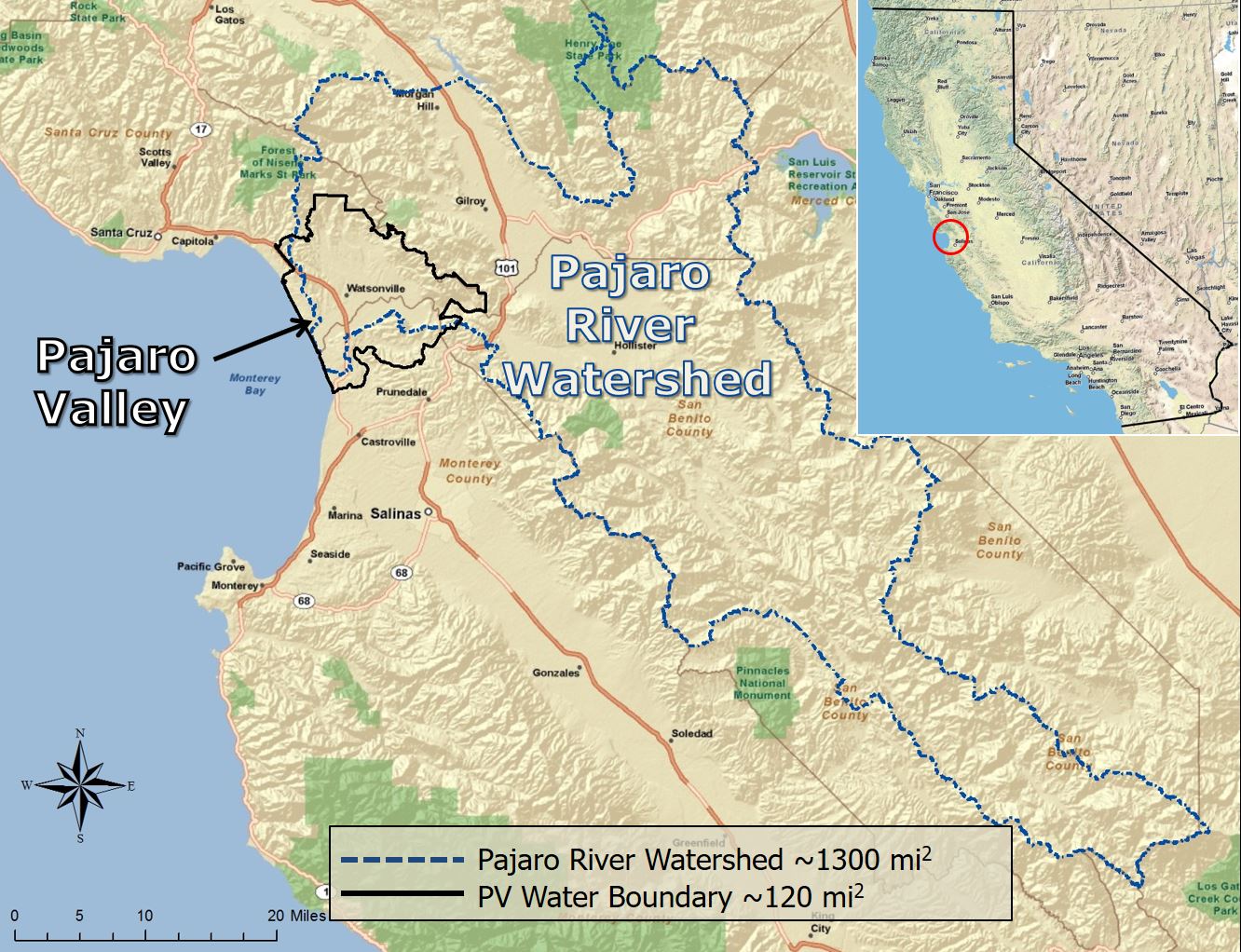
Problem Statement
As water is a limited resource, individuals, planners, scientists, and engineers must make decisions about how to allocate water for different uses. This course explores how water is allocated for agricultural, domestic, and environmental sectors by asking students to create a water plan. Student will act as planners and analyze the current and future water needs of for Parajo Valley, located in the central coast of California,. Based on this analysis, they will develop a water plan for future water use.
Module Overview
This module explores water management and planning techniques for different types of use (Urban, rural, agriculture and environmental), water sources (rain, surface water, groundwater, and recycled water) using different water management strategies (e.g. no action, water conservation, aquifer recharge, use of recycled water). The overall objective of this module is to evaluate, propose and critique current and alternative water management strategies for sustainable water use in Pajaro Valley, California.
Topics Covered
Basin Characterization.
Environmental water needs: environmental flows, instream flows, relevant ecosystems, functional flows approach, environmental flows recommendations.
Urban and rural water demand: estimating population, water use per capita, estimating urban and rural water demand.
Agriculture water demand: Reference evapotranspiration; land use, crops and crop coefficients, crop evapotranspiration, estimating agriculture water demand.
Water supplies: estimating aquifer recharge
Water budget: mass balance and aquifer storage
Baseline water budget: summary of water demands, water supply and water budget
Alternative Water Management Strategies (in development): Defining alternative water management strategies, water conservation and student's defined strategy.
Comparison of baseline and alternative water management strategies (in development).
Prerequisites
Students that take this module should know basic concepts of algebra, statistics and hydrology (desired). This module contains the first 5 assignments out of 8 of the class ESM 121 Water Science and Management, at UC Davis (class website).
Learning Objectives
At the end of this module, students will be able to appraise available water and water use in a basin, critique current and alternative water management strategies and develop a water plan.
Identify the main natural and human components of the water cycle in a basin
Estimate flows beneficial for the environment
Appraise and predict demands for human water needs
Determine the main components of a water budget: inflows, outflows and storage
Quantify how the available water is allocated among different water users (environmental, rural and urban)
Evaluate current water management scenarios and create/propose their own management strategies (in development)
Course Authors
Dr. Samuel Sandoval Solis
Sam is a professor and extension specialist in water resources at UC Davis – UC ANR, and a collaborator with the California Water Resources Institute. He is a water resources scientist interested in improving water management for human and environmental needs in California, considering the economic, environmental and social justice aspects for long term sustainable strategies. He works with a wide range of people, from farmworkers delivering training on how to prevent contamination of water due to pesticides applications (in English and Spanish), to water resources managers and decision makers developing basic research to determine environmental flows.
Email Address: samsandoval@ucdavis.edu
Dr. Freddi-Jo Bruschke
Freddi is a lecturer the Geological Sciences department as well as engineering in a Civil Engineering department at CSU Fullerton. Her background is in hydrology, environmental engineering, specifically modeling and parameter estimation of subsurface contaminant sources. Recent courses include: Physical Geology, Earth and Space Science for Teachers, Women in Engineering, Surface Water Hydrology, Surveying and Mapping Computer Applications, and Engineering Geology.
Email Address: fbruschke@fullerton.edu
Target Audience
The target audience is very broad and tiered.
Tier 1 - Upper division undergraduate students and graduate students in the following science fields: Environmental Sciences, Hydrology, Geology, Geography, Environmental Policy Analysis, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Land Use and Natural Resources Planning.
Tier 2 - Water resources managers, technical advisors and water professionals that would like to receive professional training in the development of water plans, evaluation and comparison of alternative water management strategies (in development).
Course Sharing and Adaptation
This course is available for export by clicking the "Export Link" at the top right of this page.
If you are an instructor seeking the answer keys, please contact the course creators [Samuel Sandoval (samsandoval@ucdavis.edu) and Freddi-Jo Bruschke (fbruschke@fullerton.edu)] using your official university email account, we will be delighted to share those with you.
Expected Effort and Suggested Implementation
The instructor should implement this module in five different assignments:
Introduction and Components of the Water Budget; and Introduction Environmental Water Needs (3 to 6 hours);
Components of the Water Budget - Urban and Rural Water Demands (3 to 6 hours),
Components of the Water Budget - Agricultural Demand (5 to 10 hours);
Components of the Water Budget - Water Budget and Water Plan Summary - Baseline Water Budget (5 to 10 hours);
Alternative Water Management Strategies (in development) (4 to 8 hours).
The completion of each assignment varies between 4 to 8 hours. A total of 30 to 40 hours to complete the entire module.